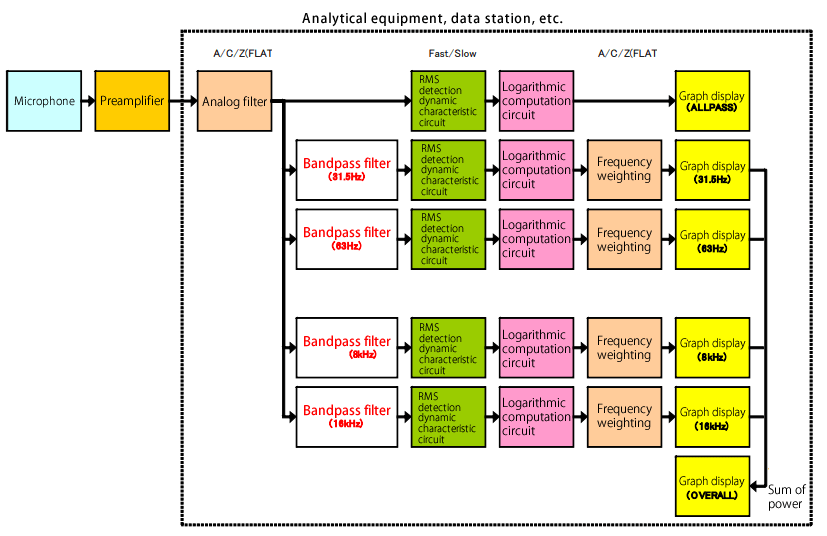
Z Frequency Weighting . If a sound is produced with. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. Often used in octave band analysis and for determining environmental noise. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. So what is the difference? this is where frequency weightings come in. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). In effect, it is like having no filter at all. This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise.
from www.onosokki.co.jp
If a sound is produced with. This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. So what is the difference? Often used in octave band analysis and for determining environmental noise. this is where frequency weightings come in. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. In effect, it is like having no filter at all. Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting.
No. 12 No.12 Frequency weighting A, C, and Z part 3
Z Frequency Weighting Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. So what is the difference? This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. Often used in octave band analysis and for determining environmental noise. If a sound is produced with. In effect, it is like having no filter at all. Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. this is where frequency weightings come in. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero).
From www.researchgate.net
Weighting frequency approximation of the ISO2631 weighting curve for Z Frequency Weighting If a sound is produced with. Often used in octave band analysis and for determining environmental noise. Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. So what is the difference? In effect, it is like having no filter at all. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. 37 rows certified sound level meters. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.onosokki.co.jp
No. 10 Frequency weighting A, C, and Z Z Frequency Weighting This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. If a sound is produced with. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Comparison of the frequency weighting derived using VPAD with Z Frequency Weighting This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. If a sound is produced with. So what is the difference? In effect, it is like having no filter at all. Often used in octave band analysis and for determining. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Frequency response of the proposed control weighting function, W u (z Z Frequency Weighting This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. 37 rows. Z Frequency Weighting.
From personalpages.manchester.ac.uk
Sound Level Meters Z Frequency Weighting This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). If a sound is produced with. this is where frequency weightings come in. So what is the difference? In effect, it is like having no filter at all. This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these. Z Frequency Weighting.
From acoustical-consultants.com
FrequencyWeighting Sound Level Measurements dB(A) vs. dB(C) Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. So what is the difference? Often used in octave band analysis and for determining environmental noise. If a sound is produced with. This is a flat frequency response. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Frequency weighting curves according to ISO 26311997 Download Z Frequency Weighting In effect, it is like having no filter at all. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. this is where frequency. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Scheme frequency weighting factor. Download Scientific Diagram Z Frequency Weighting This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might. Z Frequency Weighting.
From blog.echobarrier.com
Difference Between A, C & Z Frequency Weightings Z Frequency Weighting So what is the difference? this is where frequency weightings come in. This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z. Z Frequency Weighting.
From theproaudiofiles.com
The Fundamentals of Amplitude and Loudness — Pro Audio Files Z Frequency Weighting This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz. Z Frequency Weighting.
From blog.echobarrier.com
Difference Between A, C & Z Frequency Weightings Z Frequency Weighting This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding microphone. This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. this is where frequency weightings come in. Often used in octave band analysis and. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Frequency weighting curves of different weighting factors Download Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. So what is the difference? This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). If a sound. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Values of r.m.s. and VDV measured in the x, yand zaxis of the data Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. So what is the difference? This response replaces the older linear. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
Frequency response of the A, B, C, D, M, and RLB frequency weighting Z Frequency Weighting Frequency weightings give more weight to different frequencies. this is where frequency weightings come in. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. This response replaces the older linear or. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
1 Lateral and vertical frequency weighting functions according to W z Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). If a sound is produced with. Often used. Z Frequency Weighting.
From acousticalengineer.com
The ABCs of Frequency Weighting Acoustical Engineer Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.onosokki.co.jp
No. 10 Frequency weighting A, C, and Z Z Frequency Weighting So what is the difference? 37 rows certified sound level meters offer noise measurements with a, c and z frequency weighting. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human ear (z for zero). If a sound is produced with. This is a flat frequency response between 10hz and 20khz ±1.5db excluding. Z Frequency Weighting.
From www.researchgate.net
The simplified frequencyweighted curve. Download Scientific Diagram Z Frequency Weighting This weighting produces a flat frequency response between 10 hz and 20,000 hz, meaning that there is no alteration to the true measurement, despite how a human might really perceive the noise. This response replaces the older linear or unweighted responses as these did. This is the actual noise that is made with no weighting at all for the human. Z Frequency Weighting.